What is circuity factor?
Circuity factor is the ratio of the Network distance to the Euclidean distance between two points on the surface of the Earth.
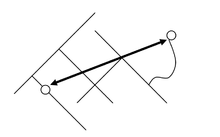
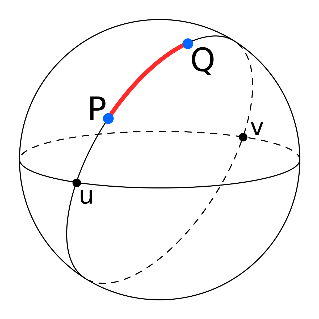
Euclidean Distance: Is the shortest path between two geographic points on the surface of the earth. It is also known as the “straight line distance” or “as the crow flies’ distance”. Although the Euclidean Distance appears straight in Fig.1 it is actually curved, since the two points are on the surface of the earth as depicted in Fig.3. However, if the two points are sufficiently nearby, the Euclidean distance appears as a straight-line. The limitation of Euclidean distance is the underlying assumption that travel along the straight-line distance is possible. Travel along the Euclidean distance may be possible for air planes, but however in a given city the travel along the straight-line distance may have obstacles such as buildings, trees, ponds and etc.
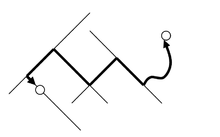
Network Distance: Is the shortest distance between two points using a transportation network for example: Roads. In Fig.2 you can see the path between points P & Q using a road network. For example, whenever you use google maps or similar applications to find directions to a destination, that application will give you directions using a road network.
Interpretation: A lower circuity factor implies that the density and connectivity of a given geographies’ road network is close to idealistic conditions (Euclidean distance). A higher circuity factor implies that the density and connectivity of a given geographies’ road network is poor. The circuity factor in urban areas with dense road networks is closer to 1 than in rural areas with sparse road network.
Observations: The key observation is that the Network distance will always be greater than or equal to the Euclidean distance. Therefore, the circuity factor which = Network distance /Euclidean distance will always be greater than or equal to 1.
Example: This is a snippet of the city I live in: Mumbai, India\
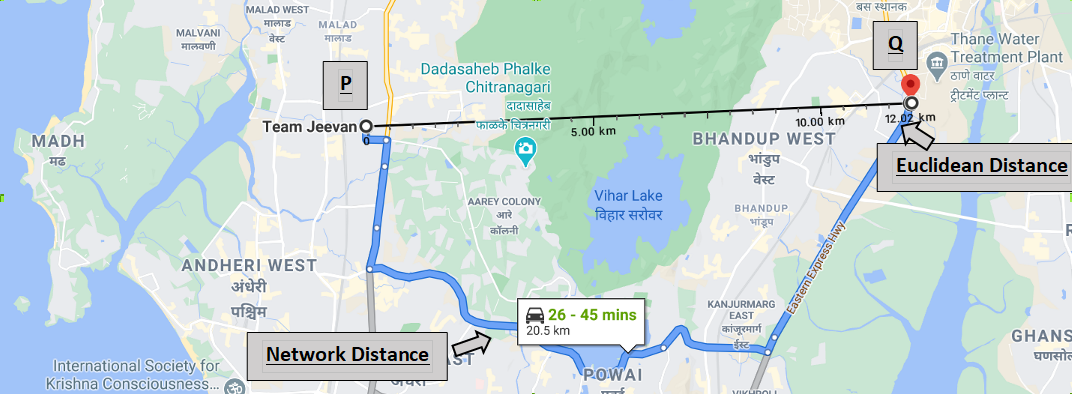
I have the Euclidean distance between P & Q (In black line) and the network distance (In blue line). As you can see the two points are divided by a forest & a lake. Hence there is no direct road network connecting the two points along the Euclidean distance (black line). The shortest road network is the blue line. Now lets calculate the circuity factor.
Network distance = 20.5 km
Euclidean distance = 12.02 km
Network distance / Euclidean distance = Circuity Factor = 20.5/12.02
Circuity Factor = 1.70
How does the CIRCUITY FACTOR TOOL Work?
The tool embedded in this website can help you determine the circuity factor of a given geography. This factor can then be used by supply chain professionals to better approximate last miles delivery solutions for a plethora of use cases. You can use this tool to determine the circuity factor for regions as small as 10 km2 in area to as big as an entire country.
This tool simply generates 5 sets of random points (origin & destination) within the rectangular overlay created by you. The tool then calculates the Network & Euclidean distance for each set of point and thereafter calculates the circuity factor for each set of points. The tool the takes an average of the circuity factors and displays it as an approximate circuity factor for the selected region.